box plot of normal distribution One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would .
Houses with colors that balance with a green metal roof have the neighborhood’s most inviting and relaxing vibe, as green symbolizes nature and progress. The metal roof stands out without compromising your house’s design, style, and look. Green metal roof works with white, yellow, stone, and taupe. With most people prefer the latter with .
0 · skewed to the right boxplot
1 · positively skewed distribution box plot
2 · positively skewed box plots
3 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
4 · how to interpret boxplot results
5 · boxplot skewed to the left
6 · box and whiskers chart explained
7 · 25th percentile on a boxplot
%PDF-1.4 %Çì ¢ 5 0 obj > stream xœ+T0Ð34R0A #9—K?È\!½˜« È3³06VÐ5±4µrÀ”¥‘ž¥¡ D™.‚K>W $q ñendstream endobj 6 0 obj 61 endobj 12 0 obj .
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the .A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with .
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
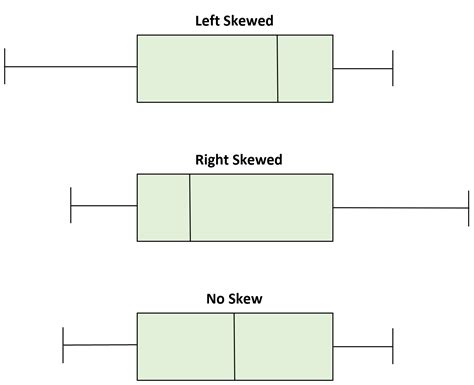
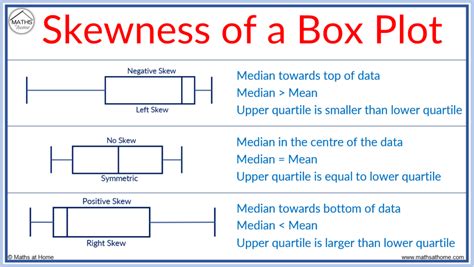
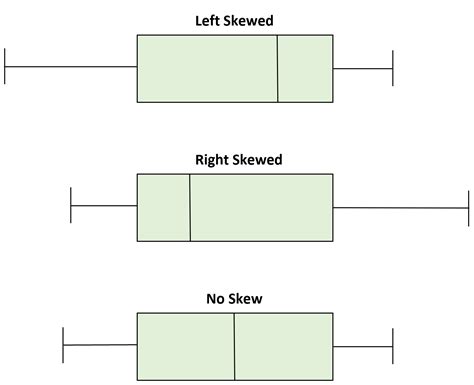
One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would .Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers .Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower .
A box plot gives us a visual representation of the quartiles within numeric data. The box plot shows the median (second quartile), first and third quartile, minimum, and maximum. The main components of the box plot are .
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would expect if you took a very large sample from that distribution.Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).
Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower or bottom quartile.
skewed to the right boxplot
positively skewed distribution box plot
A box plot gives us a visual representation of the quartiles within numeric data. The box plot shows the median (second quartile), first and third quartile, minimum, and maximum. The main components of the box plot are the interquartile range (IRQ) and whiskers.
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would expect if you took a very large sample from that distribution.
Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal. Positively Skewed : For a distribution that is positively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the lower or bottom quartile.
positively skewed box plots
positive skew vs negative boxplot
Yamaha controls are available for digital or mechanical rigs and tiller-handle controlled outboards, with some controls handling up to four outboards.
box plot of normal distribution|how to interpret boxplot results